
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW REGISTER
JBI has developed a collection of world-class resources driven by the needs of health professionals and consumers worldwide.
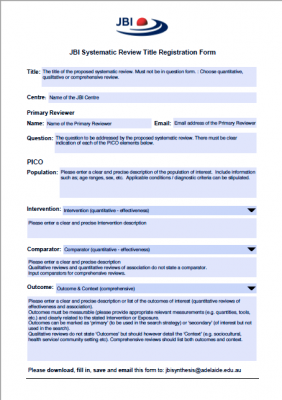
Registration of Systematic Review Titles
Please note: this register is for the use of JBI affiliated entities ONLY. Registration of a systematic review title on the JBI website is to promote collaboration between affiliated entities via highlighting current work to other JBI review authors and to recognise that the registered topic is currently in development to avoid any unintended and/or unnecessary duplication of research effort.
Registered systematic reviews that are currently underway are listed below. Protocols for these reviews may already be published or in preparation for publication within six months of initial registration. To avoid duplication, titles in this list should not be replicated by other review authors. Please contact the listed Primary Reviewer or the JBI Synthesis Science Unit if you would like further information about any of these registered reviews.
Registration of titles on this web page does not in any way constitute acceptance of the topic by JBI Evidence Synthesis.
| Title | Certified authors | Collaborating Entity or Institution | Date registered Sort descending | Custom text |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acupuncture to reduce prostate cancer treatment side effects: a scoping review | Emma Wong | The New South Wales Centre for Evidence Based Health Care: A JBI Centre of Excellence | The New South Wales Centre for Evidence Based Health Care: A JBI Centre of Excellence
Emma Wong
|
|
| Young carers in early childhood: a scoping review | Carly Ellicott | University of Plymouth Centre of Implementation Science: A JBI Centre of Excellence | University of Plymouth Centre of Implementation Science: A JBI Centre of Excellence
Carly Ellicott
|
|
| Navigating teaching and learning methods to optimize intraoperative knowledge and skills in pre-registration nursing programs: a scoping review protocol | Marlén Orsina | Centre for Transformative Nursing, Midwifery and Health Research: A JBI Centre of Excellence | Centre for Transformative Nursing, Midwifery and Health Research: A JBI Centre of Excellence
Marlén Orsina
|
|
| Influencing factors of partner participation in prenatal care of pregnant women and its impact on maternal-infant care: a scoping review | Cássia Cristina Araujo Vieira | The Brazilian Centre for Evidence-based Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence | The Brazilian Centre for Evidence-based Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence
Cássia Cristina Araujo Vieira
|
|
| Understanding the influence of pregnant women's digital health literacy on their health self-care: a scoping review | João Paulo Santana da Silva | The Brazilian Centre for Evidence-based Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence | The Brazilian Centre for Evidence-based Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence
João Paulo Santana da Silva
|
|
| Understanding the meaning of interpregnancy interval after caesarean section for women planning further pregnancies: a mixed method systematic review | Alison M Canty | The New South Wales Centre for Evidence Based Health Care: A JBI Centre of Excellence | The New South Wales Centre for Evidence Based Health Care: A JBI Centre of Excellence
Alison M Canty
|
|
| Effectiveness of neuroplastic interventions on accelerating return to play following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review protocol | Amanda Hawke | The Wits-JBI Centre for Evidenced-Based Practice: A JBI Affiliated Group | The Wits-JBI Centre for Evidenced-Based Practice: A JBI Affiliated Group
Amanda Hawke
|
|
| Measuring the social vulnerability of older people in the context of primary health care: a scoping review | Ionara do Nascimento Silva | The Brazilian Centre for Evidence-based Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence | The Brazilian Centre for Evidence-based Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence
Ionara do Nascimento Silva
|
|
| Information needs among infertile people while facing the health problem of infertility: a qualitative systematic review | Yu-Ping Hsu | Taiwan Evidence Based Practice Centre: A JBI Affiliated Group | Taiwan Evidence Based Practice Centre: A JBI Affiliated Group
Yu-Ping Hsu
|
|
| Identifying the factors and characteristics of workplace trust for healthcare workers in healthcare settings: a scoping review protocol | Nickolas J. Cherwinski | University of Victoria Collaborative for Evidence Informed Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence: A JBI Center of Excellence | University of Victoria Collaborative for Evidence Informed Healthcare: A JBI Centre of Excellence: A JBI Center of Excellence
Nickolas J. Cherwinski
|