Pregnancy-Related Urinary Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Evidence-based Exercise Interventions
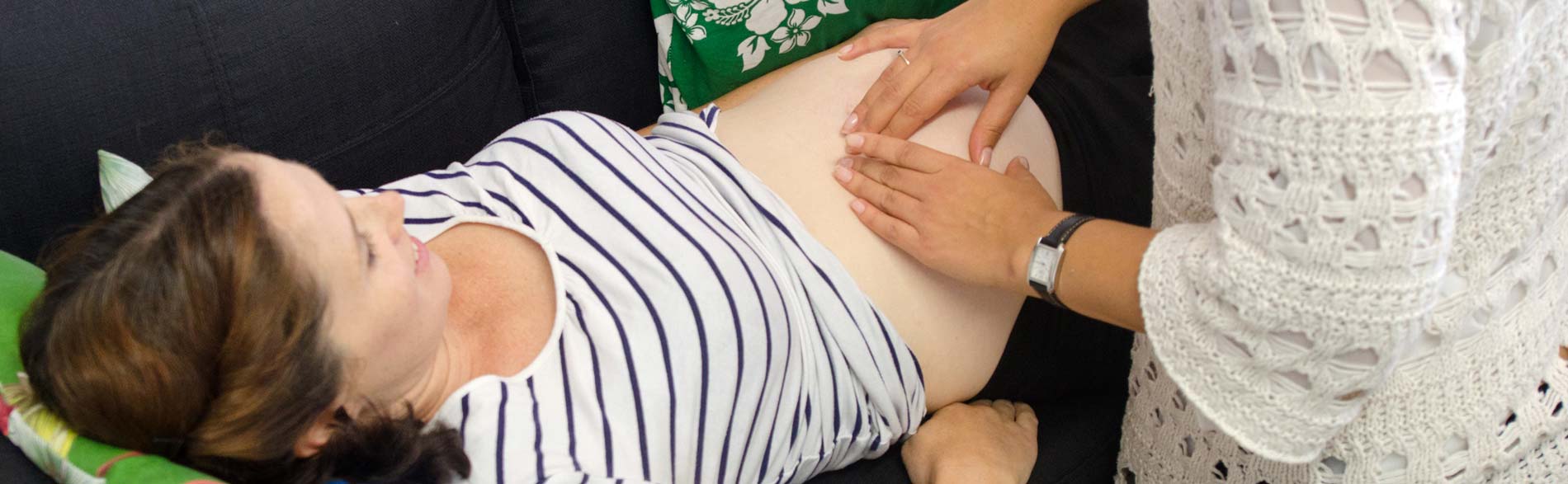
Pregnancy brings about significant anatomical changes, particularly affecting the pelvic region. The increased volume of the uterus during pregnancy often leads to stress on perineal structures, causing muscle trauma, nerve injuries, and connective tissue damage. These changes can result in pelvic floor muscle dysfunction, leading to issues like urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse.
Urinary incontinence, affecting 30% to 70% of women, increases during pregnancy but gradually decreases postpartum. Pelvic organ prolapse, characterised by the bulging of pelvic organs, affects 3% to 50% of women, with pregnancy being a known risk factor. These symptoms significantly impact women's quality of life, necessitating evidence-based guidance for healthcare professionals dealing with pregnant and postpartum women.
The Finnish national clinical practice guidelines on physical activity and exercise during pregnancy and postpartum, spearheaded by the Nursing Research Foundation, aim to unify guidance and reduce variations in care. A comprehensive umbrella review synthesises existing evidence, highlighting the effectiveness of exercise interventions for urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in pregnant and postpartum women. It emphasises the benefits of exercise and pelvic floor muscle training in preventing and treating these common issues, particularly postpartum urinary incontinence symptoms.
“The umbrella review is part of a national clinical practice guideline, which is intended for all social and healthcare professionals working with pregnant and postpartum women, especially nursing professionals working in maternity care and child health clinics. Evidence transfer and nationwide implementation of the guideline means that the competence of employees must be ensured through education and active dissemination by nurse leaders. The guideline has already been published on the internet site of the Nursing Research Foundation and in a health library that is widely used by health care professionals all over Finland; however, this umbrella review has not been published before” (Ryhtä et al, 2023)
Future steps involve integrating recommendations into Finland's clinical decision support system and incorporating guideline teachings into healthcare education programs. Additionally, the guideline serves as a valuable resource for pregnant women and their families, offering reliable information on managing pregnancy-related conditions.
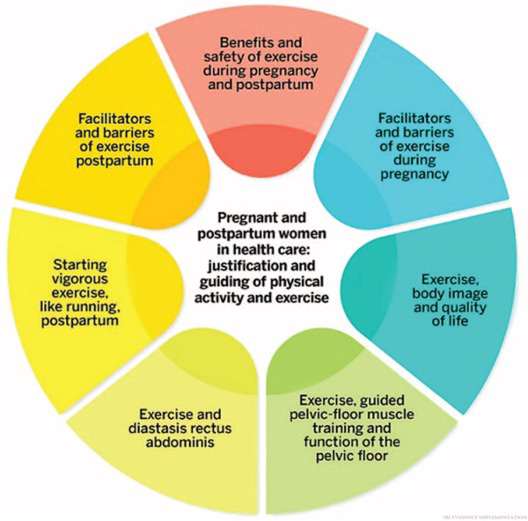
Ultimately, successful implementation of these guidelines demands comprehensive planning, resource allocation, and a concerted effort among healthcare professionals to provide holistic care for pregnant and postpartum women.
Read the umbrella review in the December 2023 issue of JBI Evidence Implementation:
Ryhtä, Iina; Axelin, Anna; Parisod, Heidi; Holopainen, Arja; Hamari, Lotta
JBI Evidence Implementation. 21(4):394-408, December 2023.